How I plan my Options trades.
I borrowed some “Planning and strategy” habits from my Business Analysis profession and corporate CEOs and tried to implement business planning process on my option trading practice, and hence, the heading: “Thinking like a CEO: Getting into my 8 step Option Trading mindset.”
My big picture idea is, Make Money, Don’t Lose It! I use eight planning components to build an option trading plan. Actual work-flow, math work and ‘thinking algorithms’ are explained separately, here in blog post my master trading plan- higher level view.
- Vision and Mission: in a manner of speaking, where am I going, as a trader? The answer to this question is vision. Mission/purpose: Why do I exist as a trader? What markets, products and ‘things’ do I trade? Personal and trading objectives and goals.
- Developing strategic mindset, concepts to embraced from ‘functional strategic planning‘ into my master trading plan.
- Identify targets, the watchlist of the Underlying I want to engage.
- Outline my quality control criteria. The justification for accepting or rejecting a trade idea from the watchlist.
- Identify tactics: the most appropriate option strategy I will use.
- Setup tactical deployment, a.k.a. risk management
- Outlines my trade management plan: How will I execute my trade?
- Exit Plan
Every trader has a vision(dream), motivation or intensified desire to achieve some goal or be someone. And, every trader has a mission, this mission must include an objective(s) and a plan to achieve these objectives. Make sure your objectives are S.M.A.R.T.
This plan outlined exactly how I will accomplish each objective. In the option trading plan, I have defined tactical mindset, targets (potential trade candidates), quality controls (my accept or reject decision), the tactic (options strategy to use out of many) to achieve objectives.
My trade setup, which is tactical deployment method to mitigate potential risks. Then comes the post trade guidance, called trade management: it is a course of action that follows executing the trade.
The last step of this plan includes the contingency plan for exiting trade prematurely.
Why? Because trade did not go exactly as I had planned and I must cut my losses, for that this exit plan is precise, and clear.
Components of my option Plan
This plan (that you are studying) is a plan tailored to my “environment” that I intend to execute. Also identify potential scenarios as possible that can threaten the achievement of my objectives.
Defining a Plan: a series of steps to achieve an objective of my an(y) option trade.
Question: Why bother to plan options trading?
Short answer: an option trade plan is the only tool to keep being a disciplined trader. It helps me to keep my fear and greed emotions at bay. An options trade plan is a solid foundation for disciplined execution of trade.
I review my master plan annually, quarterly, and monthly for following components:
- Define Purpose of trade and Duration of the option trade
- Set Reward & Risk Rules
- Create Watchlist
- Review Results’
 1. Vision and Mission: The ‘objective’ very first component of my plan!
1. Vision and Mission: The ‘objective’ very first component of my plan!

Main idea behind step 1 is to clearly define my business’s (i.e. trading) context upfront to prevent me from misunderstanding and derailing the process.
WHY TRADE? PURPOSE OF TRADING OPTIONS? I trade Options for income generation and hedging with my ‘day trading’ and ‘wealth accounts’. Not false hopes, but genuine, viable alternatives to the traditional “opportunities” out there. Set rules, take snap decisions, understand fear and avoid greed, create well defined processes and conduct research.
Outline expectations: Outline for my function, responsibilities, process, timelines and expected outcomes, right now I am the one, but if and when I have team, then I have to Identify which stakeholder(s) will ultimately sign off on strategy and capital allocation plans.
Verify the trading context by confirming the following:
Mission, which defines my trading’s broader purpose and the goals my trading work will pursue.
Vision is abstract but realistic aspirations, including underlying values, principles and beliefs that support its decision-making processes.
Set goals and objectives
Business strategy translates aspirations into:
Goals: Individual or combined undertakings that, when achieved, drive differentiated value in the longer term.
Objectives: Discrete and measurable steps that describe how I will achieve a specific goal (see blog post my master trading plan- higher level view. for the actions required for these goals/objectives).
Once clear on the trading plan, I am ready to evaluate the current state of my trading process, also known as “functional activities”, identify the future state, and set goals and objectives accordingly.
I am a professional trader, trading options, stocks, commodities, bonds, and Forex. My objective as traders is universal, that is “to make money, not to lose it!”. I have listed my three objectives as below:
- Income generation: Use Options to potentially generate income on stocks I own or want to own.
- Hedging: Options to minimize the risk on an existing stock position in my portfolio.
- Speculation: Options trading helps take a speculative market position using leverage. Surprisingly, I can even take a position that can make profits if the market stays neutral.
Every trade plan I outline must support these objectives.
The fact is, I am not going ‘win’ all trades, therefore, If, I am wrong about my trade, I want to get out of that trade with minimal loses and keep my capital to trade another better trade at some other time!
This is a universal objective and guiding commandment for my option trading. I don’t need to write it down every time.
It used to take about 20 to 30 minutes in the past when I was not using this plan. But now the planning process is understood, I hardly take more than 10 minutes to execute a trade.
 2.Strategic Option Mindset
2.Strategic Option Mindset

Developing an action plan
This is the stage at which I take my general assessment of goals and objectives and translate them into detailed action steps with assigned responsibilities. This functional action plan should be a formal document that summarizes the trading process in sequence of steps or initiatives required to accomplish a trade’s objective. This is the primary source of information for how I will execute, monitor, control and close out trades and positions.
Action plans are subject to change as surprise events occur, so I will be prepared to respond with an adaptive strategy.
Strategic trading mindset is intentional and rational thought process of ‘trading’ decision making process. For my option trading, this plan focuses on the analysis of Options pricing model, critical factors and the Greek variables that will influence the long-term success of an options trader. Similar focus is given on Forex trading decision making components.
FINDING ‘THE EDGE’ IS FIRST STEP IN SUCCESSFUL TRADING. EDGE ALLOWS YOU TO MAKE MONEY IN THE MARKETS.
EDGE IS DEFINED AS: BE A STRATEGY CENTRIC TRADER
(BASIC/RUDIMENTS: UNDERSTAND TERMS AND CONCEPTS, RULES)
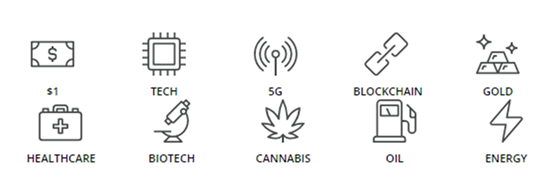
View on the market and then, express that view as market-analysis to get ‘Qualified watchlist (targets)’ with my ‘Baseline assertions’ (from market view)
Assessing my capabilities:
I Identify key functional capabilities required to execute my action plan (master trading plan). I have to self-analyze my strengths and weaknesses. This assessment should broadly align with the trading plan. Most important outcome of this step is to generate a prioritized list of functional capabilities to bolster or gaps to fill as a result of my findings.
The initiation: creating my mindset for trading options
I have been trading options only for 3 years now, there was lot of cognitive dissonance about some options trading terms, which obscured my understanding about options. I needed “some streamlined thinking process” and some “critical success factors to master”. The following terms were most difficult for me to wrap my head around:
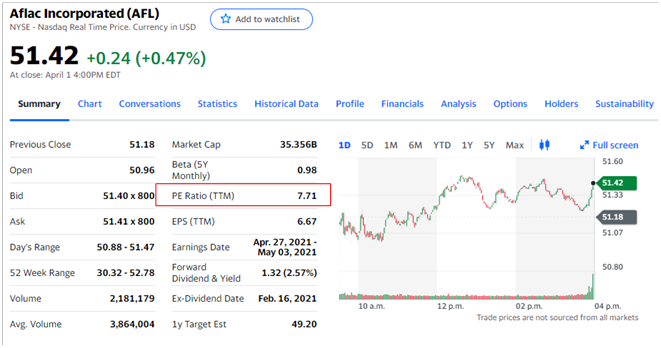
I took the following real examples from yahoo to show option’s trading example. The stock I am citing in this example is, Aflac Incorporated (AFL), listed in NYSE and Nasdaq, on April 1, 2021, closing.
AFL’s Current stock price $50
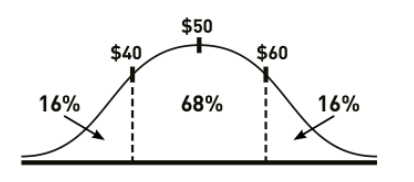
Implied Volatility (IV) is 22.8% (for simplicity’s sake let’s make IV=20%), that is annually stock will fluctuate +$10 to -$10, which is $40 to $60
This means, 68% chances that price will stay between $40-60.
Implied Volatility Rank (IV Rank):
IV rank can be compared to P/E ratio for a stock. If above AFL stock is trading around $50 per share, that is absolutely meaningless, without additional information. Is there is any way from price/share to figure out Aflac Incorporated (AFL)’s EPS (earnings per share)?
However, the P/E ratio is 7.71 tells me the earnings yield is 7.71%, similarly we can compare P/E ratio of comparable companies in Financial Services sector. (AFL is in life Insurance business) and general market.
 Rule of thumb: IV rank provides context.
Rule of thumb: IV rank provides context.
Option trade thinking:
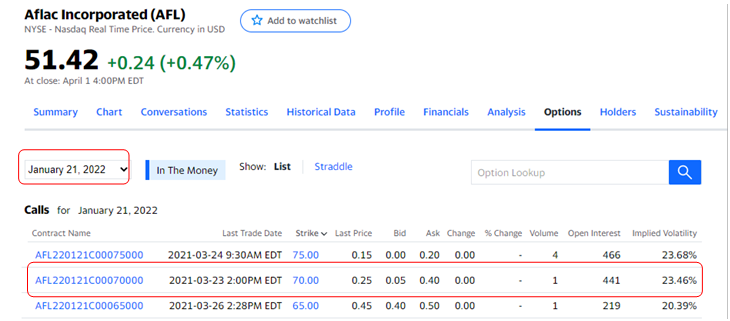
Should I purchase an AFL $70 strike call option that expires one year from today? That is, at the end of the year, if the price of AFL stock is above my $70 strike, then I can make money. Now, the million-dollar question, how much premium should I pay for AFL $70 strike call option contract? AFL’s historically, moving 22.7% per year on average. Can we expect AFL to move about same 20%?
I can see that the $70 strike call option is probably not worth much. In (OPM) Option Pricing Model likelihood of price moving to $70 is only 16% that is, chances of profits are small.
I can also see from IV of 20%, that probability price move above $60 is 16%. What is the probability of moving $20 from $50 to $70? An eyeball rough guess is about 8%. The probability of moving 2X the normal $10 move is even lower than crossing the $60 price level by next year.
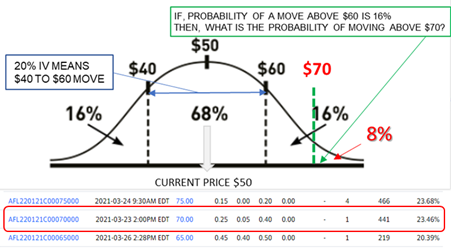
Consider this trade a lottery ticket:
This option contract costs $0.25, and the probability of success is 8%. Can I go ahead and say, “this is less of trade and more of a gamble?” Hallmark of a lottery ticket is cheap price and probability of winning a lottery is very low.
Second high volatility example Friday April 1,2021 is as below:
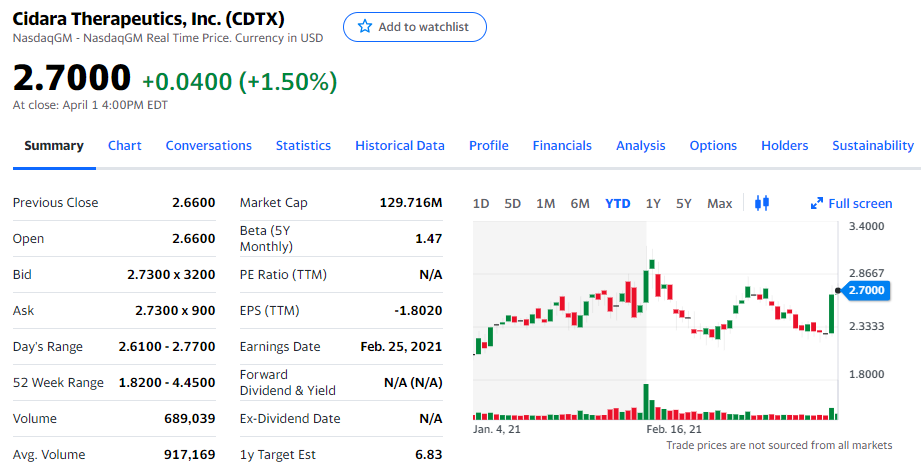
Cidara Therapeutics Inc. (CDTX) listed at Nasdaq GM
Price per share $2.70
September 17, 2021, $7.50 call strike costing %0.35 with IV 190%
Sector: Healthcare
Industry: Biotechnology
This stock is a small biotechnology company, moving as much as 180% per year. Therefore, the market might expect the same type of volatility in the future. The expected range over the next year is $5.13 up or down.
That means there is a 68% chance the stock trades between -$2.43 ($0.0) and $7.83 before its expiration on September 17,2021. There is a high probability that CDTX stock has potential to move In-The-Money at expiration.
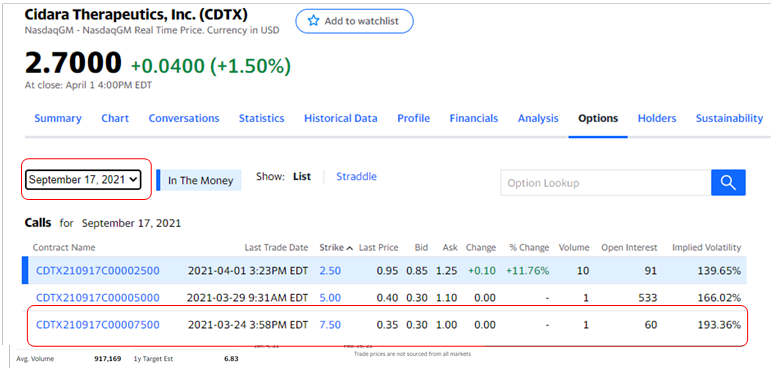
If the stock is expected to swing wildly in future, then the premium value of puts and calls options would be higher, because traders expect a higher chance of making money
 Relationship between implied volatility and an option’s price (other things being equal):
Relationship between implied volatility and an option’s price (other things being equal):
(1) When implied volatility or market expectations increase, then the option’s premium price also increases.
(2) When implied volatility or market expectations decrease, then the option’s price decreases.
The Strategic Mindset way of market analysis is one the ‘Baseline Assertion’ to take on underlying asset or the market from four categories:

Baseline Assertion depends on analysis of the current situation to create a ‘Target Qualified watchlist’ which we narrow down to find potential trading ideas. These potential trading ideas guides are considered for Tactical selection to fit appropriate option strategy.

I Start with generic my watchlist and filter that though global financial situation, sector wise analysis, broad markets, specific sectors and VIX then drill down to stocks and underlying’s within a sector using chart, fundamental, macroeconomic, and technical analysis.
3. Qualified Watchlist: Narrow down potential trade ideas.
My generic watchlist is underlying assets that are potential trade candidates for option trading positions. I will focus on eight asset classes, which is defined my Strategic Mindset. I have added Crypto currencies this year. My trading platform does not allow me to trade options on Cryptos (yet).
Asset classes I trade in
Sector analysis for leading, lagging, unusual activities etc. Depending upon my baseline assumption of being bullish, bearish, volatile, or neutral, I like to filter my watchlist for potential trade ideas based on market action, volatility, earnings, and income-based pre planned strategies.
4.QA- Quality Control

Set measures and metrics: Measure and metric are not the same, but very different.
A measure is an observable trading outcome (for example, scan for high IV trade candidates or scan for trade candidates from earnings event). Measures allow me to evaluate the efficacy of my action plans. Agree on the measures in advance to avoid reporting biases.
A metric describes the actual data collected to quantify the measure (IV Ranking, expected move % and $ amount, POP probability of profit %).
I must make sure measures and metrics are complete enough to account for a range of variables. For example, I don’t only use IV Ranking, expected move % and $ amount, POP probability of profit % to measure for watchlist. I also track critical factors, such as spread, volume, OI (open interest) and other discretionary metrics.
Market analysis results in my market-view and ‘Qualified Watchlist’ that facilitate most of trading decisions like:
- To analyze potential option trade positions
- Appropriate bias for the current market.
- Baseline assertions from market-view
- Qualifying potential trade ideas before finalizing them.
- Analyzing all potential Trade ideas through Probability, assess the potential risk, reward, and pricing scenarios of a trade before deciding to take a trade
Quality control is a “elimination Process of qualified watchlist” that will result in justification for fila trade candidates.
Why I decided to trade or reject an underlying asset.

5.TACTICAL DEPLOYMENT: Trade Execution

After my ‘Qualified Watchlist’ is narrowed down with ‘Quality control’ parameters, I end up having a final list of trade candidates.
Tactics Toolbox helps me to shortlist the most appropriate option strategy from my 20 strategies to deploy for desired position that I am planning to opening.
Many option traders deploy more than 30 strategies, but I am content with the 20 options strategies in my toolbox. How many ‘options strategies’ have you mastered and used in your options trading?
Example of tactical toolbox with 5 strategies:
| Objective | Baseline assertion | (Tactics) Strategy | Description |
| Income generation | Neutral to bullish | Covered Call | Sell a call against an existing stock position |
| Income generation | Neutral to bullish | Cash-Secured Equity Put | Sell a put, secured by cash set aside in case of assignment |
| Hedging | Neutral to bearish | Protective Put | Buy a put on an existing stock position |
Speculation | Either direction | Straddle | Buy a call and a put at the same strike |
| Speculation | Either direction | Debit Spread | Buy and sell a call at the same time, or buy and sell a put at the same time |
6. RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN

My Pre-Trade Planning, KPIs, Performance
“What I’m getting into?”
Tactical deployment is the set up for our option position. It outlines tactically what we are getting into when we enter a trade.
I think of tactical deployment as performance monitoring of trade parameters, the good, the bad and the ugly. My trade can fall into any of these parameters.
Risk Management: Risk management is integrated into the option trading plan, as risk parameters are defined below:
- I know exactly when to get out
- how much is my maximum acceptable loss is for the trade
- How I will exit or adjust the trade position to save profits or limit losses.
Defining these parameters beforehand will prevent me from getting into mental-landmines (emotions such as greed, fear, attachment to a trade etc.) to take bad decision making.
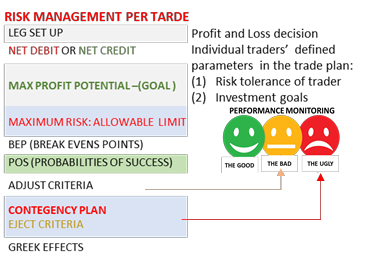
7. Mid-Course Guidance: “Trade management”

Mid-Course Guidance encompasses in trade management plan for “Risk Management parameters” in terms of profit goal and max loss, threats to success, contingency plans, and Eject Criteria.
TRADE MANAGEMENT SET FOR EACH TRADE:
| 1 | CORE STRATEGY (CHART OF UNDERLYING ASSET) |
| 2 | TREND/LEVELS SUPPLY, DEMAND, SUPPORT, RESISTANCE |
| 3 | SCORING (STEP 4) & SETUP (STEP# 5 –Tactical Deployment) |
| 4 | STRATEGY SELECTION (STEP# 4 TOOLBOX) |
| 5 | STRIKE SELECTION |
| 6 | STRATEGY CONFIRMATION |
| 7 | RISK/REWARD GRAPH (STEP 6 & 5 Trade Management & Tactical) |
| 8 | POSITION /LOT SIZE (STEP 1 account plan, lot size, Risk limit) |
| 9 | EXECUTE ORDER (STEP 6 Trade Management) |
8. Exit Plan

The Exit Plan is how we are going to get out of a trade. We never get into a fight unless we know exactly how we intend to exit. Factors for planning an exit include: a sound reason for exit, layout our closing trade set up, whether we are exiting prior to expiration or taking it all the way to expiration.
It is important to know exactly how you are going to exit a trade before the volatility of the markets get the better of you.
Passive Exit when:
1. my initial stop-loss is hit
2. When my target-profit is hit
3. When trade parameters no longer valid
Active Exit when:
4. My trailing-stop is hit
5. When trade parameters are no longer valid
6. Volatility based Exit approach using (ATR)
7.Roll into next contract
Planning Complete
That’s the plan! It’s just a logical sequence of steps that encapsulates and memorializes our research, lays out the playing field for the trade, sets risk tolerance tripwires for action while in the trade and lines out how we will exit. Don’t trade without one!
Once you have the system down it will take 5 -10 minutes max to complete and will keep you aligned very closely with our universal objective.
References and links:
What is Strategic Planning? Definition and Steps – TechTarget
The Planning Process – Principles of Management | OpenStax
Garter -9 Steps to Successful Functional Strategic Planning
Asana – 7 strategic planning models, plus 8 frameworks to help you get started
Leave a Reply